Want to be ahead of the headlines?

100 Days of War: the Sanctions Response to Russia’s Invasion
100 days into Russia’s (second) invasion of Ukraine, how has the international sanctions response changed? What should you expect for the next 100 days? Reduced focus on individuals, prioritization of broader economic sanctions, and efforts to enforce existing restrictions will all play a role.

What Are Countries Doing to Counter Russia’s War?
Over 140 countries voted against Russia’s war at the UN, but only 45 have imposed sanctions against Russia. Why? There is the question of political will, but a more immediate explanation is the fact that most countries do not have an autonomous sanctions program, instead relying on the UN or EU to adopt sanctions which they implement.

Russia Is Now the World’s Most Sanctioned Country
Russia Is Now the World’s Most Sanctioned Country. The crippling economic sanctions which targeted Iran were adopted over the course of nearly 10 years. Half of the sanctions adopted against Russia have been implemented in the course of 10 days.
Russia is now subject to over 5000 different targeted sanctions, more than Iran, Venezuela, Myanmar and Cuba combined.

Impact of Sanctions on Russia
The EU, US, Australia, Canada, Japan, Singapore Switzerland and others imposed over 2200 new sanctions against Russian politicians, oligarchs, banks and energy and defense firms since February 22 bringing the total of Russia-focused sanctions to over 4000. Russia is now more sanctioned than North Korea. Data updated as of 28 February, 8AM EST.

Sanctions in Response to Russian Invasion of Ukraine #2
Castellum.AI is seeking to provide a resource compiling sanctions data targeting Russia for its ongoing invasion of Ukraine. Data updated as of 26 February, 9 PM ET.

Sanctions in Response to Russian Invasion of Ukraine #1
Castellum.AI is seeking to provide a resource compiling sanctions data targeting Russia for its ongoing invasion of Ukraine. Data updated as of 25 February, 11 AM ET.

Incident Response & Sanctions Navigating Ransomware Risks
In October 2021, the US Treasury's sanctions authority, the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC), issued sanctions compliance guidance for the cryptocurrency industry. Castellum.AI has helped its users meet or exceed the specific steps mentioned in the guidance document recommendations since January 2021.
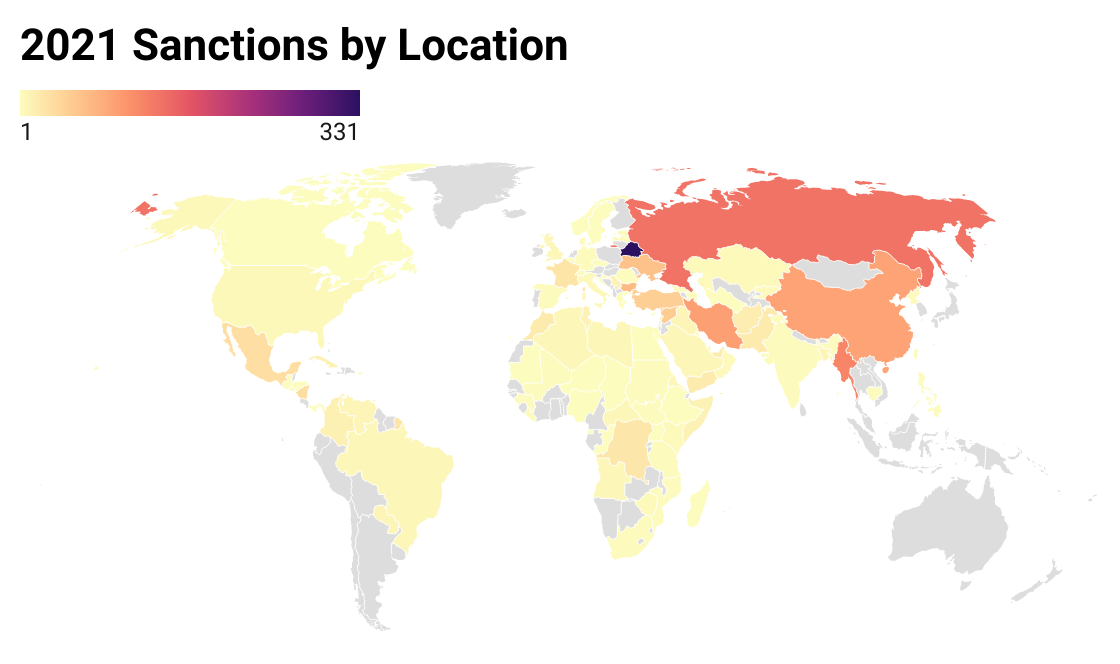
2021 Sanctions in 12 Charts
In 2021 China rapidly grew its sanctions program, the US and EU renewed focus on corruption and human rights abuses globally, the US increased its crypto offensive and for the first time in perhaps a decade, Iran was not a major focus. See this and more to round up the year in global sanctions.
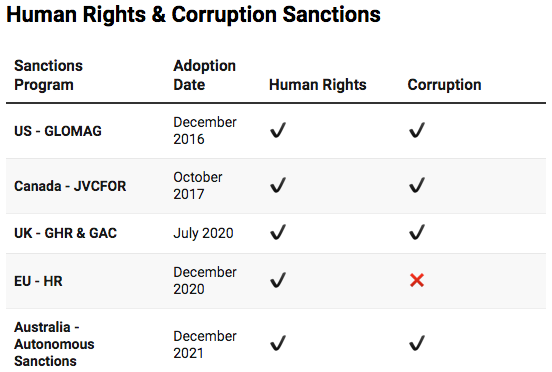
Human Rights Sanctions in 5 Charts. Who Applies Them, and Where?
Sanctions programs focused on human rights and corruption are increasingly at the forefront of the public debate. However, the data shows significant disparities between designations between US, UK, EU, and Canada programs. These graphs show the distribution and depth of each human rights sanctions program to date in preparation for Human Rights Day.
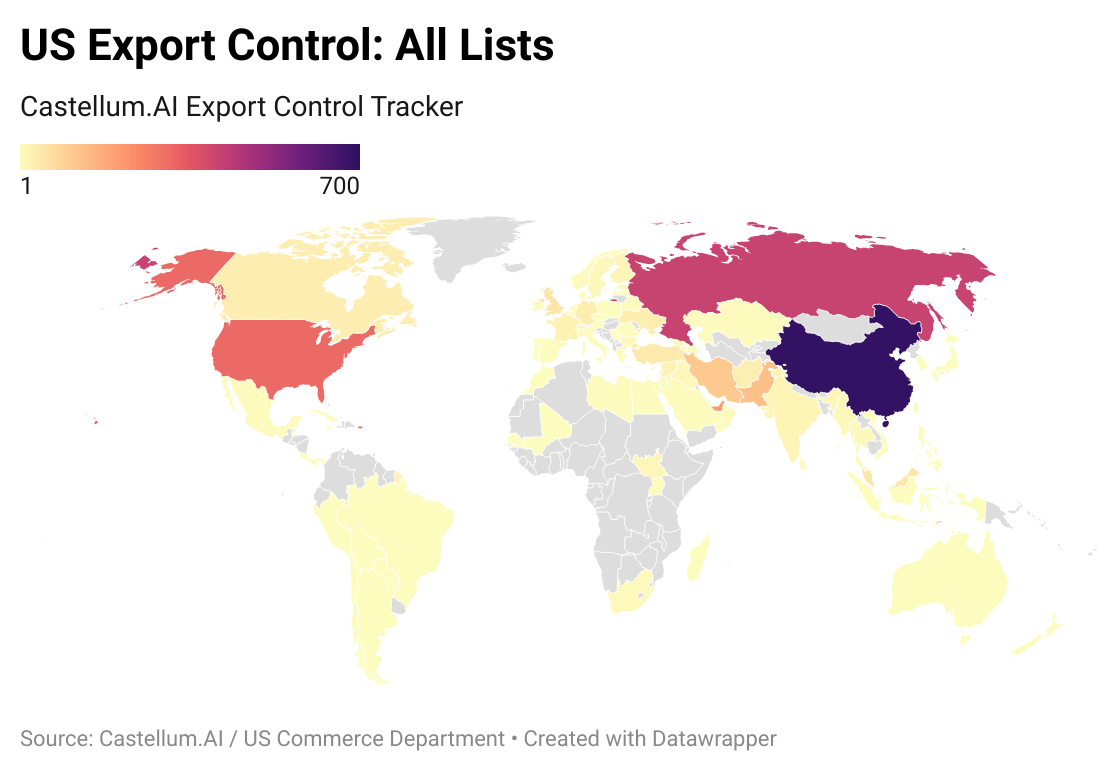
Export Control Tracker Fourth Edition: November 2021
Commerce announced the addition of 31 entries to the Entities List in November, including eight firms in China involved in the development or acquisition of quantum computing capabilities and 16 China- and Pakistan-based entities involved in Islamabad’s nuclear program. BIS additionally reached an agreement with a US-based firm over unauthorized exports to Huawei in the bureau’s first enforcement action since the 2019 adoption of export controls against the Chinese tech firm.
